Messsenger RNA (mRNA)of sequence of four different bases of nucleotides.A triplet of three bases is called a codon that encodes a specific amino acid.The sequence of these triplets specifies a specific sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide synthesized from it ,which is known as genetic code.In other words, the genetic code is the correspondence of codons (code words)to definite amino acids.Since there are four different bases,the number of sequence of three of them is 4^3 or 64.The genetic code exhibits the following features.
The code is universal,that is all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms use same codons to specify each amino acid.
More than one codon can code for same amino acid.Therefore genetic code is said to be degenerative.
Genetic code is nonoverlapping,that is adjacent codons do not overlap.
Out of 64 possible triplet codons,one is start codon(AUG)and three are nonsense or stop codon(UAA,UAG,UGA).
Sense codons and non-sense codons
The codon which specify a particular amino acid is known as sense codon.
Out of 64 codons,61 are sense codon.
Sense codon can be read by t-RNA.
Sense codon(especially AUG)is responsible for initiation of translation and elongation of amino acid sequence.
The codon which do not correspond to any amino acid is known as non sense codon.
The three non sense codons are UAA,UAG and UGA.
Non sense codon cannot be read by t-RNA.
Non sense codons are responsible for termination of translation.
lijit search
GENETIC CODE
Posted by milan at 1:22 AM 0 comments
ANTIGEN AND ANTIBODY
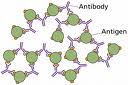
An antigen or immunogen is any substance that is capable of stimulating the production of specific antibody with which it may chemically combine.Usually this response involves the formation of antibodies or highly specialized T-cells.The two important properties of antigen are specificity and immunogenecity.Specificity is the ability to react specifically with immune response and immunogenecity is the capacity to stimulate an immune response.The low molecular weight chemical compound which is capable of reacting with the specific antibody but incapable of inciting an immune response by itself is known as hapten.
The majority of antigens are protein (nucleoproteins,lipoproteins,glycoproteins or polypeptides)or polysaccharides with molecular weights greater than 10,000 daltons.The above mentioned compounds may be capsules,cell walls,flagella,pili and toxins of bacteria.
Antibodies are synthesized by host B lymphocytes and plasma cells when they come in contact with a foreign antigen.Antibodies are defined as specialized serum glycoproteins that are formed in response to an antigen and react specifically to that antigen or one very closely related to it in some observable manner.Chemically antibodies are globulin and hence they are called immunoglobulins.Immunoglobulines comprise 20-25%of the total serum proteins.Antibodies consists of four polypeptide chain two identical heavy chains or ‘H’chain and two identical light chains or ‘L’chains linked by disulphide bonds.Each peptide chain consists of variable region and constant region.Varaible region is the antigen binding site and constant region is complement fixation site.
Anitbodies have wide range of functions and use which are-
Elimination or removal of foreign antigen from the circulation.
Recruitment and enhancement of host effectors mechanism.
Measurement of antipathogenic antibody levels in diagnosis.
Passive administration of antibodies for host protection
Posted by milan at 1:11 AM 0 comments
Bacterial recombination

Genetic recombination is the process by which parts or all of the DNA molecules from two separate sources are exchanged or brought together into a single unit.Genetic recombination involving bacteria is known as genetic recombination.In bacterial recombination,the cells do not fuse.Instead only a portion of the chromosome or naked DNA from the donor cell is transferred to the recipient cell.Inside the recipient cell,the donor DNA fragment is positioned alongside the recipient DNA in such a way that homologous genes are adjacent.Enzymes act on the recipient DNA,causing nicks and excision of a fragment.Then the donor DNA is integrated into the recipient chromosome in place of the excised DNA.The recipient cell then becomes the recombinant cell because its chromosome contains DNA of both the donor and the recipient cell.
Bacterial recombination occurs from three different ways.
- Conjugation
- Transduction
- Transformation
The uses of genetic recombination are:
- Genetic recombination maximizes the diversity of genotypes among progeny.
- The ability to generate new genotypes in rapidly changing environment allows the members of bacterial population to grow in presence of toxins,antibiotics,phages and to exploit new environment.
Posted by milan at 1:09 AM 0 comments
Steps involved in replication of DNA

DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is a rope like molecule composed of two strands,each wound around the other to form a double helix.
DNA has the ability to produce identical copies of itself synthesizing complementary to its original template.
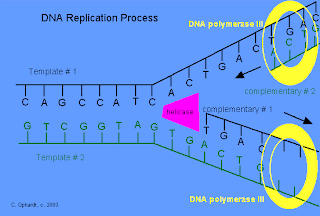
Replication is a semiconservative process in which each of the two helices formed from the parent double strand have one old and one new strand.DNA replication requires a DNA template,a primer,deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates(dATP,dGTP,dTTP,and dCTP),mg++,ssb protein(single strand binding protein)and enzymes such as helicase,DNA gyrase,primase,DNA polymerase I and III,and DNA ligase.
- Bidirectional replication starts in the first step from the origin which allows an entire chromosome to be replicated in half the time it would take if the replication were unidirectional.
- At the initial stage,the DNA double helix is opened up and the initiation of the DNA replication occurs on the two single strand.as the replication proceeds,the replication fork appears to move down the DNA.
- At the replication fork,double helix DNA is unwound and a small single stranded region is formed by helicases.the single stranded protein is complexed wiyh ssb protein which stabilizes the single stranded DNA.
- The action of a superhelix relaxing protein DNA gyrase relieves the strain imposed by the unwinding of the strands.
- A primer,short sequence of RNA serves as a template as RNA polymerase unlike DNA polymerase ,requires only template but not primer.
- Deoxyribose nucleotides are then added the 3’ end of the RNA primer and the main DNA strand is synthesized on the DNA template.This strand is complementary to the DNA strand and is synthesized by DNA polymerase III
- The enzyme DNA polymerase I now degrade the RNA primer and simultaneously catalyze the synthesis of a short DNA segment to replace the primer.This segment is then joined to the main DNA strand by a DNA ligase.
- DNA replication always proceeds from 5’phosphate to 3’hydroxyl.On the strand growing from 5’phosphate to the 3’ hydroxyl called the leading strand,DNA synthesis can occur continuously because there is a 3’-OH at the replication fork to which new nucleotide is added.But on the opposite strand,called lagging strand,DNA synthesis occur discontinuously and a short pieces of DNA called okazaki fragments are synthesized.The okazaki fragments are joined by polynucleotide ligase,a joining enzyme to form a continuous strand.
Posted by milan at 1:29 AM 0 comments
Blood agar medium
It is a differenltial media that is prepared by adding blood in the nutrient agar.It does not involve pH related reactions but differentiates hemolytic and non haemolytic bacteria.The lysis of RBC produces a clear zone around the colony growing on the blood agar plate.Some of the bacteria can produce haemolysin that lyses red blood cells.Examples ,species of Streptococcus that reside harmlessly in the throat often cause a hemolysis called alpha hemolysis,which is characterized by a zone of greenish clearing around the colonies.
MacConkey agar
It is a differential media that differentiates between lactose fermenter and non-lactose fermenter.this agar contains lactose as a source of carbon.Those organisms that can utilize lactose for its carbon metabolism thereby producing lactic acid produce pink colonies and those that cannot utilize lactose produse yellow colonies.This is mainly due to the presence of pH indicator neutral red which is red or pink in acidic condition and yellow in alkaline pH.
The presence of bile salts and crystal violet in MacConkey agar inhibit the growth of Gram positive bacteria,allowing the selective growth of gram negative bacteria.Thus,MacConkey agar is also known as selective media. In addition to the selective growth of enterobacteria,MacConkey agar also differentiates lactose fermenting bacteria from non lactose fermenting bacteria.
Posted by milan at 2:26 AM 0 comments
CULTURE MEDIA AND ITS TYPES USED UN MICROBIOLOGY LAB.
The common ingredients found in culture media are agar,peptone,meat extracts,yeast extract,carbohydrates,mineral salts,buffers,pH indicators and water.
Culture media can be classified on the basis of chemical composition,use and physical state.
On the basis of physical state
Solid media:
Major solidifying agent is in solid state that contains agar.These media contains 1.5% agar.this form of media is mainly used in Petri dishes as plate cultures.They are used to observe the colony characteristics,size,shape of microorganisms and also for the isolation and enumeration.e.g.MacConkey agar,blood agar,etc.
Semisolid media
These media are gelatinous in nature with jelly like consistency.These are prepared by adding 0.2-0.5%agar to a fluid medium.These media are used for motility test and for different biochemical test.e.g.SIM media,Hugh and Leifson’s media.
Liquid media
It does not contain any solidifying agent or any agar.growth of the organisms are shown by the turbidity in the medium.Generally,liquid media are used for the propagation of a large number of microorganisms,for the transfer of microorganisms.e.g.peptone water,MacConkey broth,nutrient broth etc.
On the basis of chemical composition
Natural media
Those media whose chemical composition is not known are called natural media.It contain all necessary ingredients for growth of microorganisms,but they are in crude form.They are more useful for cultivating unknown bacteria,as it usually provides full range of growing factors such as amino acids,polypeptides,vitamins and minerals.
Synthetic media
Media prepared by adding precise amount of highly purified inorganic or organic chemicals to distilled water are synthetic media.So chemical composition is known in this media.This media are of great importance in studying the metabolic activity of microorganisms.Examples include enrichment media,Czapek and Richard’solution.
Semisynthetic media
The media of which chemical composition is partially known is as semisynthetic media.e.g.nutreint agar,PDA,Czapek Dox agar,etc.
On the basis of utility purpose
General purpose media
Selective media
Differential media
Enriched media
Enrichment media &transport media
Posted by milan at 2:11 AM 0 comments
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA ACCORDING TO ITS CELL WALL
Cell wall of bacteria is defined as the rigid structure present below the capsules,sheaths and flagella and external to the cell membrane of the cell that gives shape to the cell.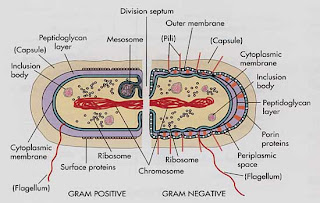
Cell wall accounts for 10-40% of dry weight of the cell.On the basis of composition, bacteria can be divided into two major groups i.e.gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
The original distinction between this two bacteria is based on the gram staining reaction.The rigid layer in the cell wall of bacteria is called as peptidoglycan or merein.
Each layer of peptidoglycan is a thin sheets of two sugar derivatives,N acetyl glucosamine and N acetyl muramic acid and a small group of tetrapeptide consisting of L-alanine,D-alanine,D-glutamate and and either lysine or diaminopimelic acid.
The rigidity of the cell wall is provided by glycosidic bond between two sugar derivatives.An unusual feature of bacterial cell wall is the presence of two amino acids that have D-configuration,D-alanine and D-glutamic acid since amino acids are always in L-isomeric form.
Cell wall of gram positive bacteria
Peptidoglycan,content is high in gram positive bacteria as 70% of the dry weight of its cell wall,is of thickness 10-20nm.Besides peptidoglycan cell wall contains polysaccharides that are covalently linked to peptidoglycan e.g.Streptococcus pyogens also the wall of Streptococcus aureus contains teichoic acid.
Teichoic acid is an acidic polysaccharide composed of ribitol phosphate or glycerol
Phosphate.Teichoic acids are negatively charged that binds with magnesium ions and thus protect from thermal injury.Teichoic acid binds with lipids which are known as lipoteichoic acids.Lipid content is less in gram positive bacteria except Mycobacterium,corynebacterium etc.These bacteria are rich in mycolic acid.
Gram negative bacteria
Peptidoglycan layer is much thinner.Lipopolysaccharide is present in outer membrane.also in outer membrane porins are present which act as pores for particular molecules.There is a space between the layers of peptidoglycan and the secondary cell membrane called the periplasmic space.Flagella if present have four supporting rings instead of two.Techoic acids or lipotechoic acids are not present as in gram positive bacteria.
Lipoproteins are attached to the polysaccharide bone.Most of the gram negative bacteria do not sporulate.
Posted by milan at 1:38 AM 1 comments
TRIAL FAILED FOR AIDS PREVENTING GEL
The trial took four years and involved 9,385 women in four African countries.The gel had no effect as,amongst the total,4.1 percent who used it were infected.
PRO 20000,the microbicide,is a polymer of naphthalene sulphonate which is described as"a large sugary molecule with a charge on it"which clinged on the shell of the virus to receptors.But the microbicide had given few hopes as it worked nearly perfectly on cells in lab and in monkeys.
Women from South Africa,Zambia,Uganda and Tanzania were recruited in the trial.Among them some of them from general population,some were from highway truck stops,and some were those infected from their husband.All of them were given condoms and told to try to use them before any sex act,which made such trials take far longer and produce much less robust results.Researches prediction 20 years ago for making a safe,acceptable,effective microbicide has
has proved to be far more difficult.Sometimes prostitutes get men to use condoms but wives or lovers cannot and may also want to become pregnant without being infected.
But now researches are beginning to test gels and rings containing antiretroviral drugs like tenofovir,dapivirine and maraviroc.The advantage of those is that they are very good potent and attack different parts of the virus.
The new gels being tested must be inserted before an sometimes after sex.
Executive director of AVAC,Mitchell Warren called the results disappointing,but said the large trial would pave the way for future ones.
Posted by milan at 1:15 AM 0 comments
FACTS ABOUT BACTERIA
- Many of us don't know that the human gut is home to 1-2 kg of bacteria.While the surface area of our intestine is bigger than a tennis court.
- In a sputum sample the first group of bacteria we see are a group of anthrax bacilli.
- As known,the air is full of bacteria and in the recent discoveries it is seen that bacteria spend their whole lives growing and reproducing in the clouds above our heads,in the atmosphere.
- Of all bacteria,99% are helpful.
- Helpful vaccines are made of dead or weakened bacteria and viruses.
- Bacteria produce nearly half the oxygen in the atmosphere.
- We humans have more microbes on our body than on the planet.
Posted by milan at 1:42 AM 0 comments
WONDER DRUG
Penicillin works by interfering with the formation of the bacteria's cell wall while it is growing,weakening the wall and killing the bacteria.It is used to treat infections like ear infections.
But despite of its usefulness it's use can make birth control pills less effective,resulting in pregnancy.Penicillin also don't treat a viral infection such as flu.
Penicillin should be taken carefully,your doctor must be given informations about the drugs used:e.g.methotrexate or probenecid etc.

Posted by milan at 1:23 AM 0 comments
GERM THEORY OF DISEASES
Even in the 16th century,it was thought that something could be transmitted from the diseased person to healthy person that induced disease.Many disease is seen to spread through population and were contagious and the unknown agent that did the spreading contagion.
The credit for the earliest discovery of pathogenic role of microorganisms probably goes to Augustino Bassi,who proved that the disease in silkworm was due to fungul injection.
Oliver Wendell Holmes in 1843 reported that puerperal sepsis a disease of child birth.
Holmes and ignaz in 1846 published a book for the antiseptic solutions.
L.pasteur found that fermentation of fruits and grains,resulting in alcohol,was brought by microbes and also determined that bacteria were responsible for the spoilage of wine during fermentation,and this work led to the germ theory of disease.
Joseph lister,concluded that wound infections too were due to microorganisms.He developed system to prevent microorganisms from entering wounds by the application of antiseptics.In 1876,a german physician,Robert Koch introduced methods for isolation of pure strains of bacteria.The most notable contribution of koch was the establishment of the casual relationship between a microorganism snd a specific disease applying a set of criteria referred to as koch’s postulates.And for many of his contributions he is known as father of medical microbiology.
Posted by milan at 1:04 AM 0 comments
MAJOR CONTRIBUTIONS IN MICROBIOLOGY
- Invention of microscope in 1673 by Antoni Van Leewenhook made it possible to view the small creatures that existed,which were expected long before.
- During 300BC,Aristotle believed that organisms might have originated spontaneously from the soil,plants or others.
- About 40BC,Virgil gave directions for the artificial propagations of bees.
- During this period it was an accepted fact that maggots might have developed by exposing meat to warmth and air, but Francisco Redi doubted this fact. For which he experimented and gave his view that maggots originated from flies and not the meat.Which undoubtedly settled the controversy of spontaneous generations.
- In 1749 John Needham observed the appearance of organisms on meat exposed to hot ashes that were not present at the start of the experiment and concluded that bacteria originated from the meat.
- In the 17th century L.spallanzi kept the boiled beef in the flask which was sealed,which showed no microbes.And this discouraged spontaneous generation.
- Edward Jenner in 1798 succesfully demonstrated vaccination.Due to this contribution most of the industrialized world was free of smallpox.
- After some 60 years,this was again answered by two scientists Schulze and Schwann.
- Both the scientists passed air through strong acid and red hot tubes separately into the flask.In neither of the cases,microbes appeared.But taught that acid and heat changed the air,so cannot support growth.
- Similarly in 18th century scientists like Schroeder,T.Von Du sch and Poucher gave their own view about the spontaneous generation.
- Irritated by the Pouchet’s logic and data,that gave an extensive report that proved its occurrence,Louis Pasteur performed the experiment that ended the argument for all time,and proved that microorganisms are not spontaneously generated from inanimate matter.
- And in 1877,John Tyndall gave final blow to spontaneous generation.
- A fascinating and fortunate accident for the discovery of wonder drug penicillin was the major contribution of Sir Alexander Fleming of England 1929.
Posted by milan at 1:01 AM 0 comments
Proof that microbes cause disease
- Louis Pasteur in1857 proposed "germ theory"of disease.
- Joseph Lister introduced antiseptics in surgery.He introduced the method to spray carbolic acid on surgical instruments,wounds and dressings,and thus reduced surgical mortality due to bacterial infections.German bacteriologist cultivated anthrax bacteria using blood serum at body temperature,outside the body.On the basis of pasteur's "germ theory" he published "Koch's postulates".This postulates was known critical test for the involvement of a microorganisms in a disease
- In every case of the disease the agent must be present.
- The agent must be isolated and cultured in vitro.
- When a pure culture of the agent is inoculated into a susceptible host,the disease must be reproduced.
- And the agent must be recoverable from the infected host.
pure culture techniques and culture media
Posted by milan at 1:42 AM 0 comments
Introduction of Microbiology
Microbiology is the branch of biology that deals with the study of microorganisms.
It deals with all the branches of the tiny organisms that are useful or harmful in one and many ways,could be cultured or non culture able.Microbiology started along with the development of microscopy.
Development of microscopy
Many scientists in the initial stage believed that living organisms could develop from non-living material.
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek in 1676 was the first scientist to observe microorganisms.
Spontaneous generation controversy
Initial stages in the development of microorganisms led to many controvers
 is.The foremost controversy was spontaneous generation of microorganisms.Fransisco Redi in 1688 was the first person who,during his experiment,found and refuted that organisms did not originate if kept carefully away from flies.
is.The foremost controversy was spontaneous generation of microorganisms.Fransisco Redi in 1688 was the first person who,during his experiment,found and refuted that organisms did not originate if kept carefully away from flies.Finally in 1861 fomous scientist Louis pasteur used swan necked flask which finally proved that microorganisms do not arise from spontaneous generation.And which eventually led to
- Development of sterilization
- Development of aseptic technique
Posted by milan at 12:42 AM 0 comments