
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is a rope like molecule composed of two strands,each wound around the other to form a double helix.
DNA has the ability to produce identical copies of itself synthesizing complementary to its original template.
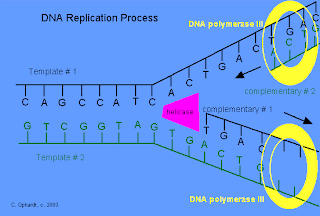
Replication is a semiconservative process in which each of the two helices formed from the parent double strand have one old and one new strand.DNA replication requires a DNA template,a primer,deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates(dATP,dGTP,dTTP,and dCTP),mg++,ssb protein(single strand binding protein)and enzymes such as helicase,DNA gyrase,primase,DNA polymerase I and III,and DNA ligase.
- Bidirectional replication starts in the first step from the origin which allows an entire chromosome to be replicated in half the time it would take if the replication were unidirectional.
- At the initial stage,the DNA double helix is opened up and the initiation of the DNA replication occurs on the two single strand.as the replication proceeds,the replication fork appears to move down the DNA.
- At the replication fork,double helix DNA is unwound and a small single stranded region is formed by helicases.the single stranded protein is complexed wiyh ssb protein which stabilizes the single stranded DNA.
- The action of a superhelix relaxing protein DNA gyrase relieves the strain imposed by the unwinding of the strands.
- A primer,short sequence of RNA serves as a template as RNA polymerase unlike DNA polymerase ,requires only template but not primer.
- Deoxyribose nucleotides are then added the 3’ end of the RNA primer and the main DNA strand is synthesized on the DNA template.This strand is complementary to the DNA strand and is synthesized by DNA polymerase III
- The enzyme DNA polymerase I now degrade the RNA primer and simultaneously catalyze the synthesis of a short DNA segment to replace the primer.This segment is then joined to the main DNA strand by a DNA ligase.
- DNA replication always proceeds from 5’phosphate to 3’hydroxyl.On the strand growing from 5’phosphate to the 3’ hydroxyl called the leading strand,DNA synthesis can occur continuously because there is a 3’-OH at the replication fork to which new nucleotide is added.But on the opposite strand,called lagging strand,DNA synthesis occur discontinuously and a short pieces of DNA called okazaki fragments are synthesized.The okazaki fragments are joined by polynucleotide ligase,a joining enzyme to form a continuous strand.
0 comments:
Post a Comment