An antigen or immunogen is any substance that is capable of stimulating the production of specific antibody with which it may chemically combine.Usually this response involves the formation of antibodies or highly specialized T-cells.The two important properties of antigen are specificity and immunogenecity.Specificity is the ability to react specifically with immune response and immunogenecity is the capacity to stimulate an immune response.The low molecular weight chemical compound which is capable of reacting with the specific antibody but incapable of inciting an immune response by itself is known as hapten.
The majority of antigens are protein (nucleoproteins,lipoproteins,glycoproteins or polypeptides)or polysaccharides with molecular weights greater than 10,000 daltons.The above mentioned compounds may be capsules,cell walls,flagella,pili and toxins of bacteria.
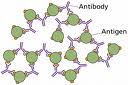
Antibodies are synthesized by host B lymphocytes and plasma cells when they come in contact with a foreign antigen.Antibodies are defined as specialized serum glycoproteins that are formed in response to an antigen and react specifically to that antigen or one very closely related to it in some observable manner.Chemically antibodies are globulin and hence they are called immunoglobulins.Immunoglobulines comprise 20-25%of the total serum proteins.Antibodies consists of four polypeptide chain two identical heavy chains or ‘H’chain and two identical light chains or ‘L’chains linked by disulphide bonds.Each peptide chain consists of variable region and constant region.Varaible region is the antigen binding site and constant region is complement fixation site.
Anitbodies have wide range of functions and use which are-
Elimination or removal of foreign antigen from the circulation.
Recruitment and enhancement of host effectors mechanism.
Measurement of antipathogenic antibody levels in diagnosis.
Passive administration of antibodies for host protection
0 comments:
Post a Comment